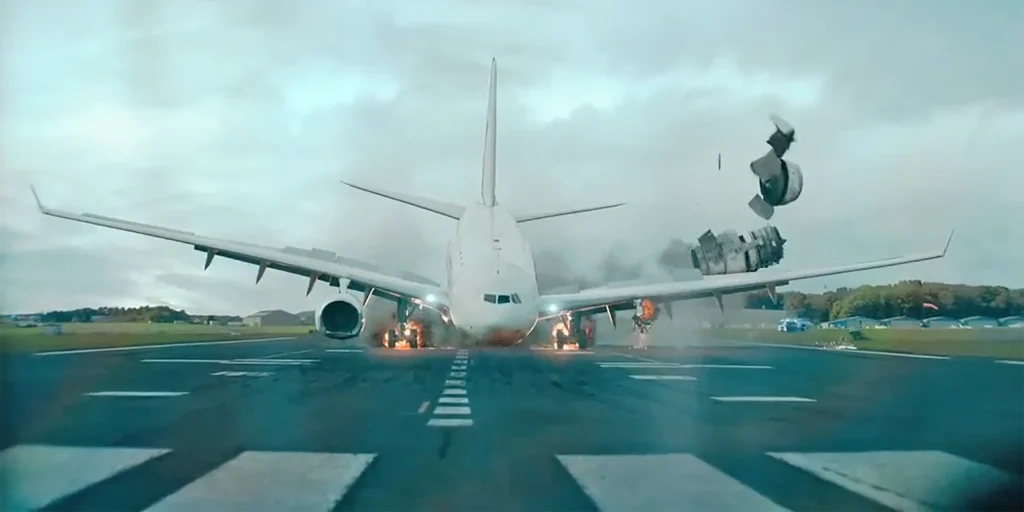
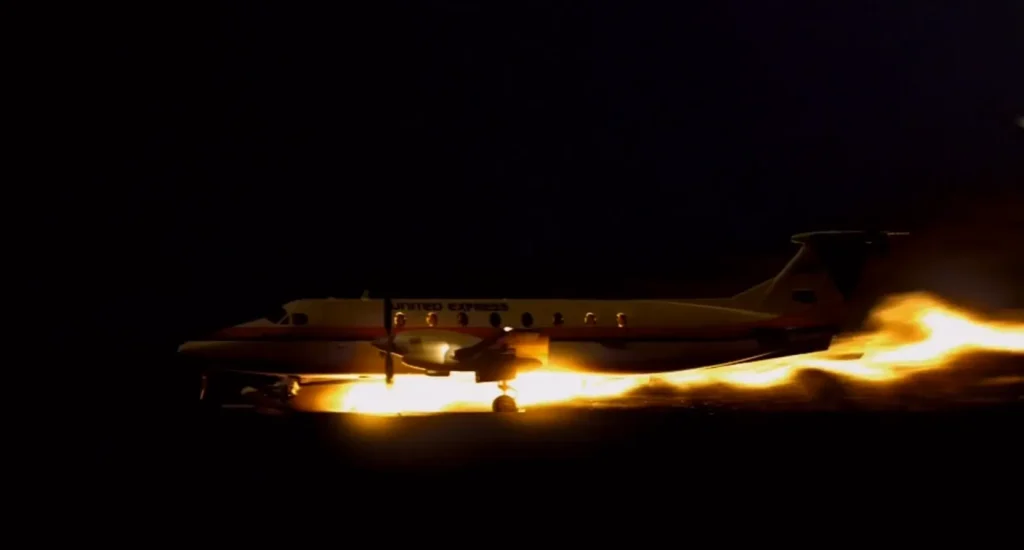
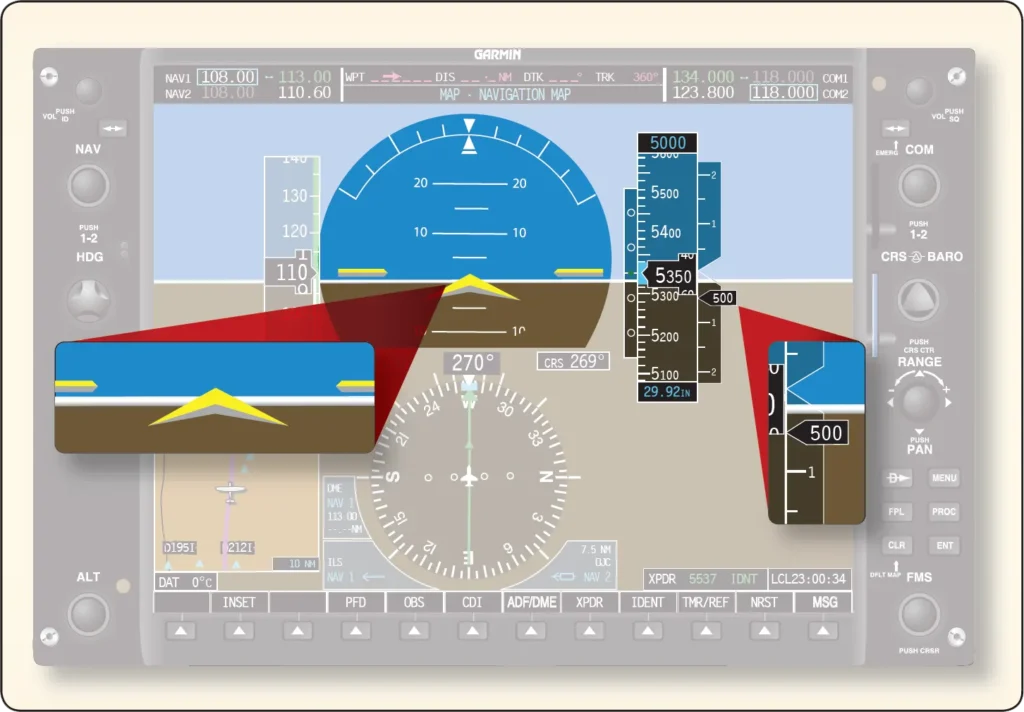
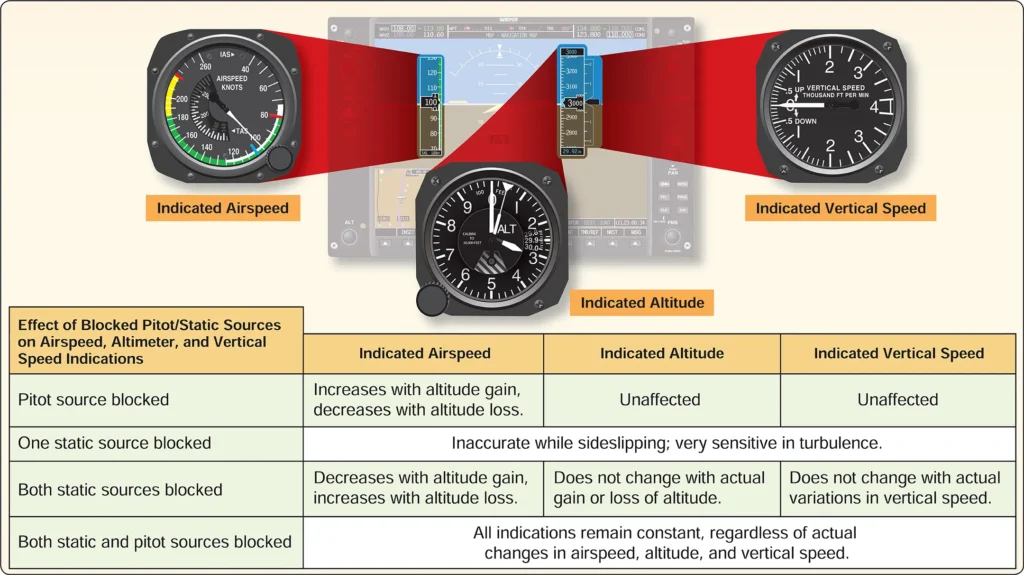
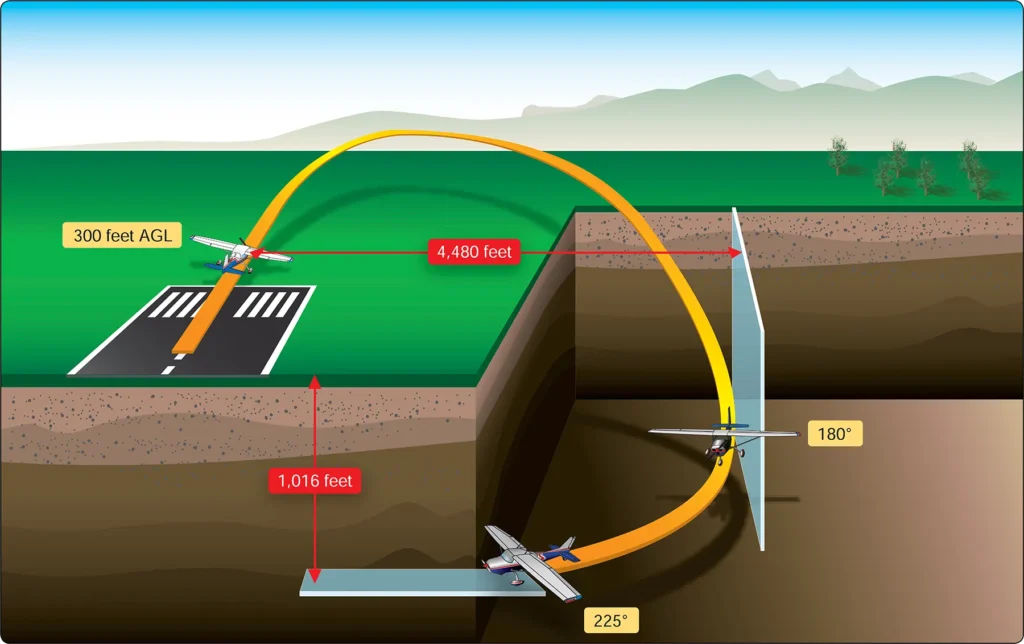
Airplane Emergency Response Systems
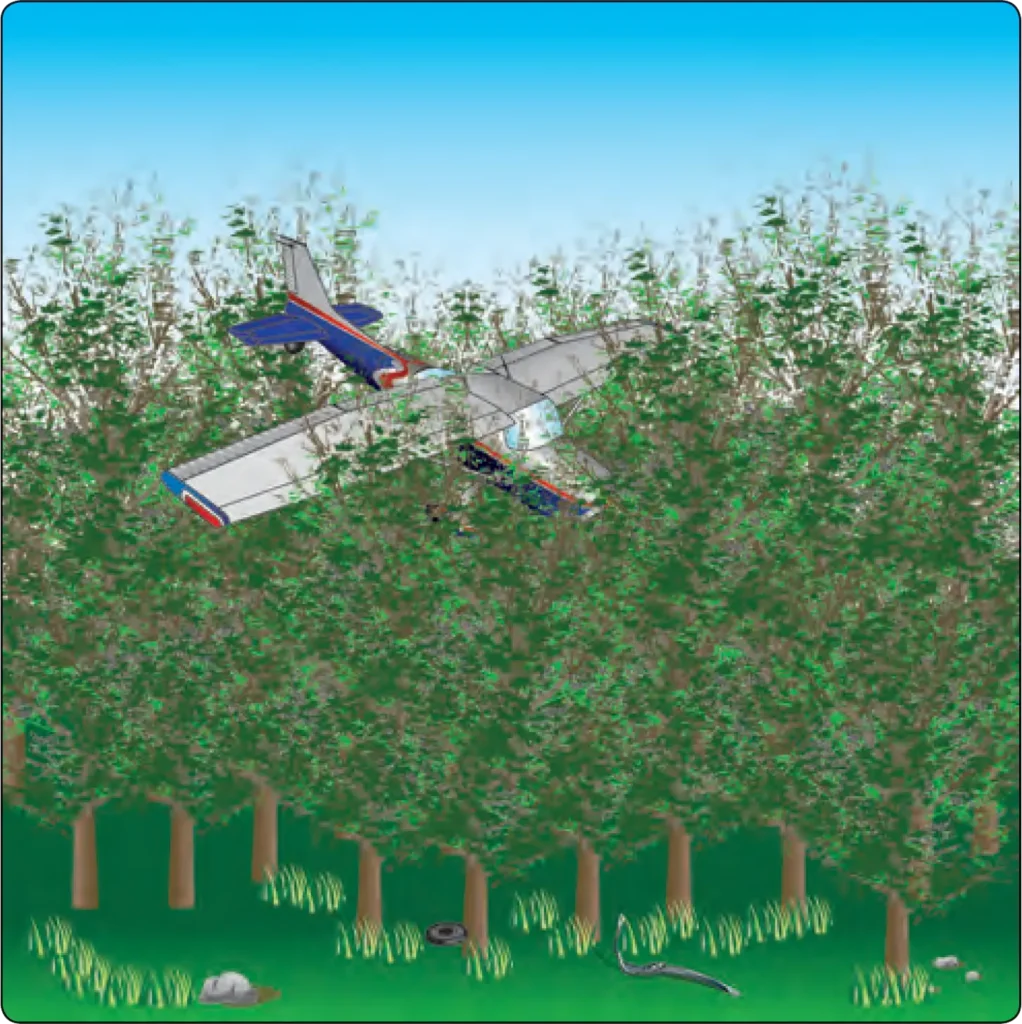
Airplane Flying, Flying TrainingAirplanes may have installed systems that provide alternatives in certain emergency situations. For example, ballistic parachute systems, if installed, may be deployed in an emergency allowing an airplane to descend slowly enough toward the ground such that occupants usually survive the resulting impact with minor or no injuries. Airplanes may also have an Emergency Autoland […]