Path and Terminator Concept | Airborne Navigation Databases
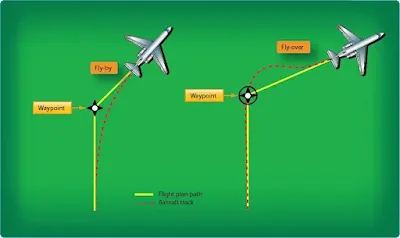
Flying Training, Instrument ProceduresThe path and terminator concept is a means to permit coding of terminal area procedures, SIDs, STARs, and approach procedures. Simply put, a textual description of a route or a terminal procedure is translated into a format that is useable in RNAV systems. One of the most important concepts for pilots to learn regarding the limitations […]
Path and Terminator Concept | Airborne Navigation Databases Read Post »