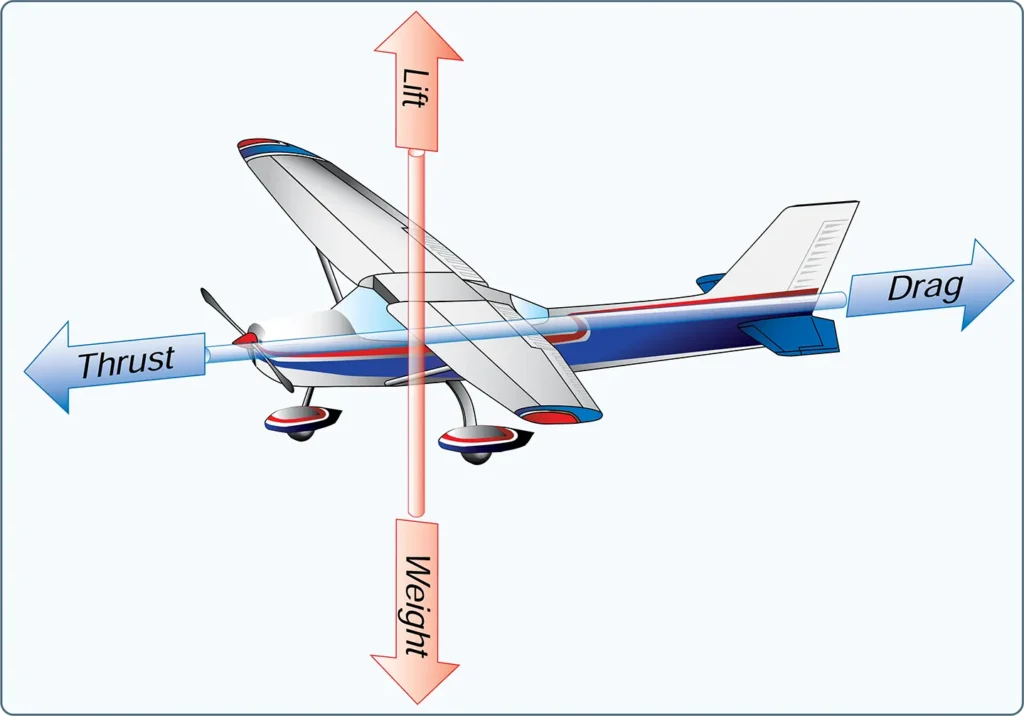
Forces Acting on the Aircraft
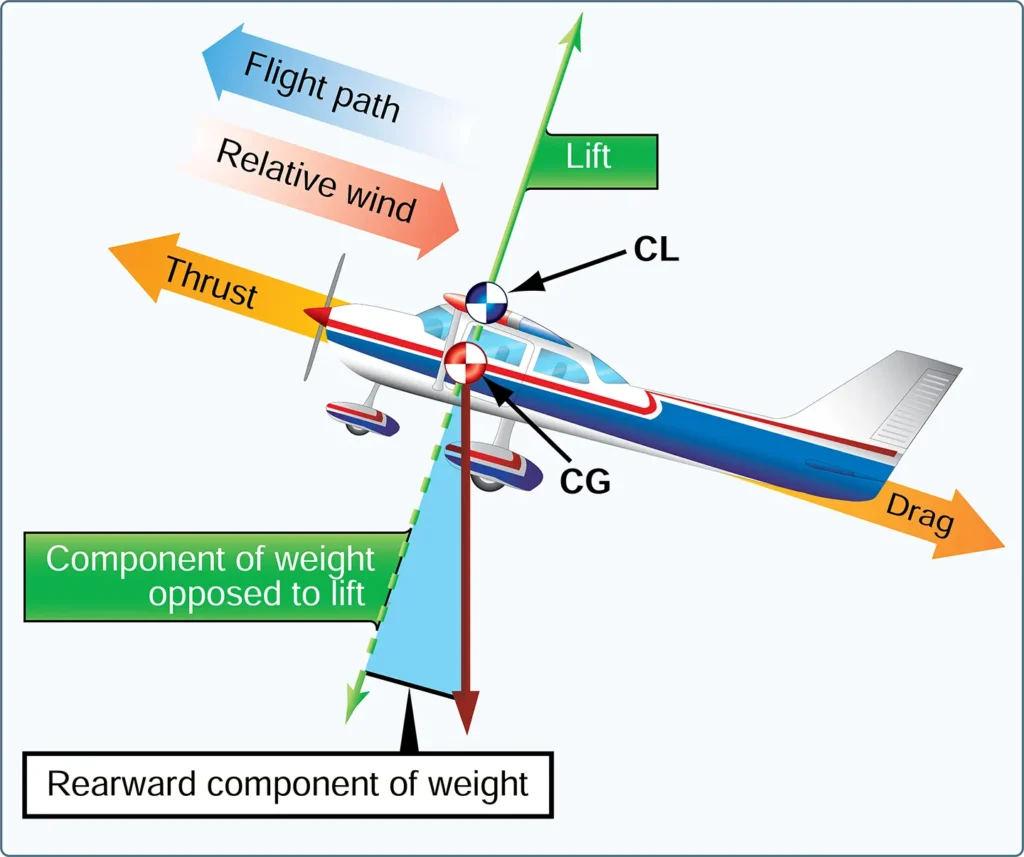
Aeronautical Knowledge, Flying TrainingThe four forces acting on an aircraft in straight-and-level, unaccelerated flight are thrust, drag, lift, and weight. They are defined as follows: Thrust—the forward force produced by the powerplant/ propeller or rotor. It opposes or overcomes the force of drag. As a general rule, it acts parallel to the longitudinal axis. However, this is not […]